Learn How to Managing Diabetes: Understanding the Types, Symptoms, Treatment, Complications, and Prevention
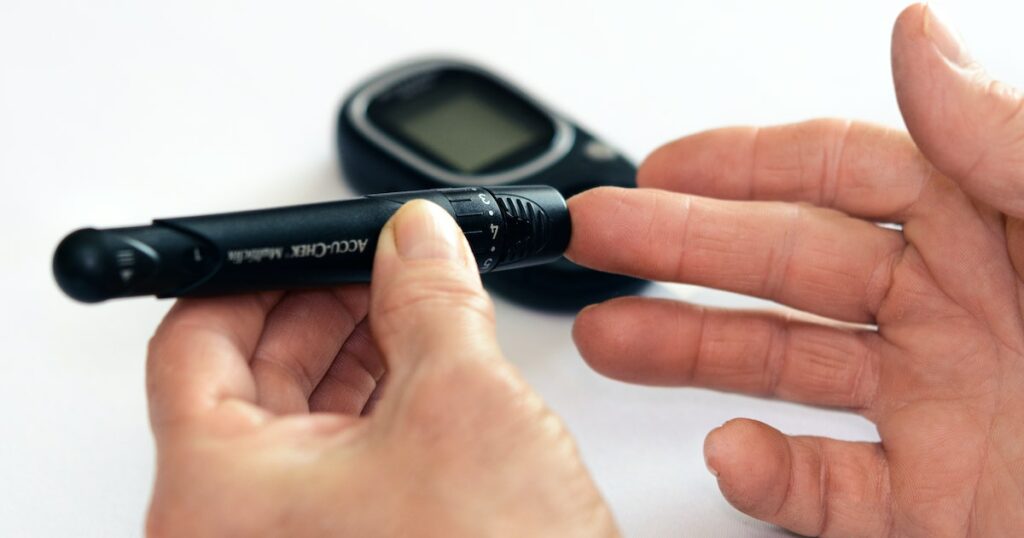
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It happens when your body is unable to create enough insulin or when it is unable to adequately use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that aids your body’s digestion of sugar, which is the primary source of energy for your cells. Sugar builds up in your system when you don’t have enough insulin, causing a variety of health concerns.
Diabetes Types:
Diabetes is classified into three types: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, begins when your immune system erroneously assaults and destroys insulin-producing cells in your pancreas. As a result, your body is unable to create enough insulin to keep your blood sugar levels stable. Type 1 diabetes is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can strike at any age.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms include:
• frequent urination
• excessive thirst
• extreme hunger
• unexplained weight loss
• fatigue
• irritability
• blurred vision
• slow healing of cuts and bruises
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is normally treated with daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump. It is also critical to frequently monitor your blood sugar levels, exercise regularly, eat a nutritious diet, and avoid smoking and alcohol.
Type 2 Diabetes
The most frequent kind of diabetes is type 2. It happens when your body is unable to utilize insulin efficiently or produces insufficient insulin to regulate your blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is mostly diagnosed in adults, though adolescents and teenagers are becoming more common.

